Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion, Kepler's Law of Orbits, Angular Momentum of Satellites, Kepler's Law of Areas, Areal Velocity of Planets, Kepler's Law of Periods and Explanation of Kepler's Laws.
Important Questions on Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Assume that the earth moves around the sun in a circular orbit of radius and there exists a planet which also move around the sun in a circular orbit with an angular speed twice as large as that of the earth. The radius of the orbit of the planet is
The period and radius of a circular orbit of a planet about the sun are related by
A satellite is launched into a circular orbit of radius R around the earth. A second satellite is launched into an orbit of radius (1.01)R. The period of the second satellite is larger than the first one by approximately
Figure shows the motion of a planet around the Sun in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at the focus. The shaded areas and are also shown in the figure which can be assumed to be equal. If and represent the time taken for the planet to move from to and to , respectively, then
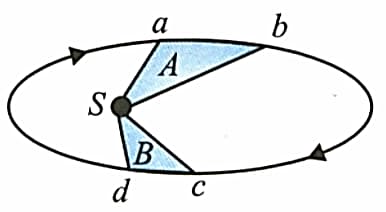
Which is constant, the earth revolving around the sun?
The period of revolution of planet around the Sun is times that of. The distance of from the Sun is how many times greater than that of from the Sun?
The distance of two planets from the Sun are and metres respectively. The ratio of time periods of these two planets is
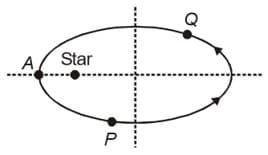
A planet revolves around a massive star in the elliptical orbit shown. Point A on the orbit corresponds to perigee. Consider motion of the planet from position P to position Q. About A, angular momentum of the planet
Two satellites are in the parking orbits around the earth. Mass of one is times of the other. The ratio of their periods of revolution is
In planetary motion, the areal velocity of position vector of a planet depends on angular velocity and the distance of the planet from sun . If so, the correct relation for areal velocity is:
A planet is revolving around the sun in an elliptical orbital as shown in the figure. At which point will its be maximum?
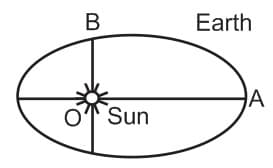
The earth moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit as shown in the figure. The ratio, . The ratio of the speed of the earth at and at is
Two satellites and are revolving around a planet in coplanar and concentric circular orbits of radii and respectively in the same sense. Their respective periods of revolution are and respectively. The radius of the orbit of A is equal to . What is their relative speed when they are closest?
A planet of the sun is in a circular orbit around the sun, midway between the sun and the earth. Then
If the distance between the earth and the sun becomes half its present value, the number of days in a year would have been
The time period of a satellite of earth is . If the separation between the earth and the satellite is increased to the previous value, the new time period will become -
The time period of a satellite of earth is . If the separation between the earth and the satellite is increased to times the previous value, the new time period will become
Halley's comet has a period of 76, had distance of closest approach to the sun equal to . the comet's farthest distance from the sun if the mass of sun is kg and in MKS units is
A satellite is revolving round the earth in an orbit of radius with time period . If the satellite is revolving round the earth in an orbit of radius with time period then
The period of a planet around sun is times that of earth. The ratio of radius of planet's orbit to the radius of earth's orbit is:
